Links aren’t just clickable text—they’re signals that shape your site’s search performance. But not all of these signals carry the same weight. Some help boost your authority; others keep it steady and clean. In my 9+ years in SEO, I’ve seen firms misuse link types and cost themselves trust and rankings. I wrote this to clarify when each type of connection matters, how search engines react, and what strategies you need to get results—without crossing into spam territory.
What You’ll Learn
- What dofollow links do and why they matter
- What nofollow tags are and when they make sense
- How each type affects your site’s standings
- How and when to apply each tag
- Simple steps to identify them on any page
- Why Google’s 2019 update changed tagging forever
- FAQs based on real questions I get daily
- Pro tips to use these tags strategically in your content
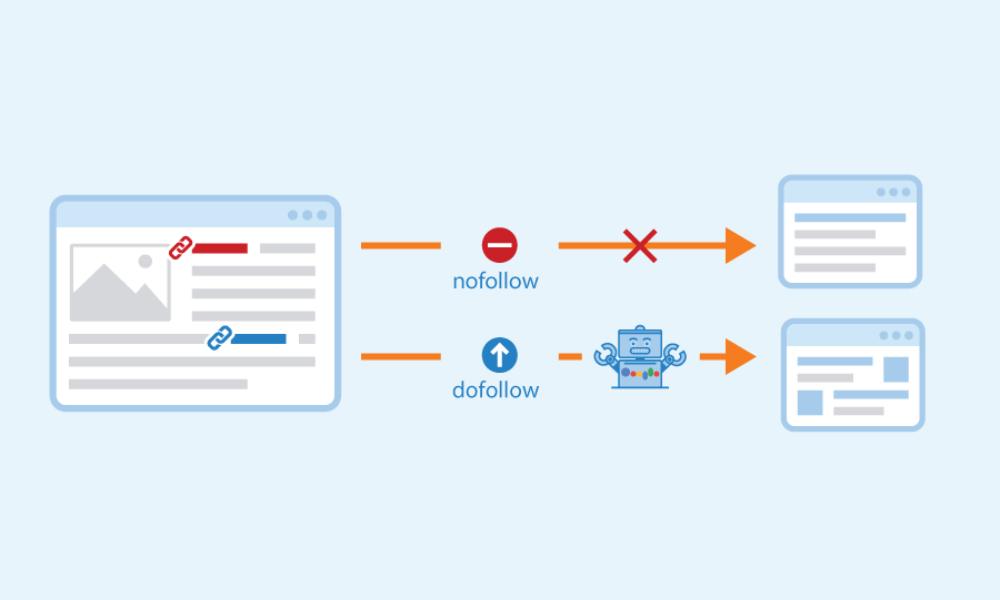
1. What Are Authoritative Links? (Dofollow)
By default, every hyperlink you create tells Google: “Go ahead and follow this.” That’s what traditional links do—they pass credibility and can move your site up in rankings. Getting a link from a respected source? That’s like a mini endorsement. I learned long ago: quality over quantity matters most. A few well-placed links from authoritative domains can outperform dozens from unknown or irrelevant sites.
Want to learn how to earn links that genuinely impact your SEO goals? Check out my guide on building links the right way: High‑Quality Backlinks Without Spammy Tactics.
2. When to Use Non-Endorsing Links (Nofollow)
The “no” tag is simple: it tells crawlers, “I’m linking, but I’m not backing this.” It was originally created to fight spam in comments and forums. Now it’s a tool in your toolkit. I apply it when linking to content I don’t fully endorse—like paid advertisements, user-submitted updates, or unverified sources. However, it doesn’t block all benefits. These links can still generate clicks and visibility, and sometimes they lead to real endorsements later.
3. Comparing the Two: A Side-by-Side Snapshot
| Aspect | Authoritative (Dofollow) | Neutral (Nofollow) |
| SEO credit passed? | ✅ Yes | ⚪ Mostly no |
| Default behavior | ✅ | ❌ |
| Best for trusted, editorial links | ✅ | ❌ |
| Best for paid, generated, or uncertain links | ❌ | ✅ |
| Can still drive traffic? | ✅ | ✅ |
Note: Since 2019, Google treats the no-tag as a “suggestion”—so it might occasionally count one in its ranking formula if it fits the context.
4. Strategic Tagging: How to Decide
I’ve helped brands fine-tune their outbound linking hygiene with these rules:
- Editorial goodwill: Use the default tag when linking to quality, vetted sources.
- Sponsored content or ads: Always add rel=”nofollow” to paid placements or affiliate links. It’s safer and keeps you in Google’s good books.
- User-contributed text: Use the tag on forum posts, blog comments, or any section where your team isn’t sure of link quality.
- Mixed signals: Even if you’re linking to a noteworthy source, use the tag if you’re mentioning them in a paid or sponsored context.
Tagging everything nofollow? That screams spam defense, not quality. Tagging nothing? That looks manipulative. Balance is key.
5. How to Spot Link Types (3 Quick Methods)
- Inspect Element: Right-click the link and check the rel= attribute.
- Browser Extensions: Tools like “NoFollow Simple” or the Ahrefs toolbar highlight tags instantly.
- Auditing Tools: SEO crawlers (like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb) list both link types to guide your cleanup.
These checks are standard when I audit clients, and you should run them quarterly.
6. Why Google’s 2019 Update Changed Everything

Google formally announced that they no longer treat rel=”nofollow” as a strict directive—but rather as a hint. This means they might credit such links during ranking calculations if they seem editorially earned. In practice, that means:
- Don’t rely solely on the tag to pass—or block—all SEO power.
- Aim for natural citation patterns, not strict rules.
- Keep your linking strategy clean and transparent.
Nofollow still matters, but the world isn’t as binary as it once was.
7. Real Questions I Hear from Clients
- Do these tags hurt my rankings?
No. The main risk is overuse, which signals suspicion to search engines. - Can I get tagged links converted into credit-passing ones?
Yes. You can ask the webmaster to remove the no-attribute or hope Google views it favorably. - Do links from social platforms matter?
Most are tagged nofollow—but they still bring referral traffic and exposure. - Should I tag every external reference?
No—that’s lazy and unnatural. I favor selective, thoughtful use.
8. Advanced Tips for Tag Management
- Automate: Work with developers to auto-append tags on sponsored or user-generated links.
- Track in GA: Monitor outgoing link clicks to understand which generate interest—even if tagged neutral.
- Mix it up: A healthy site has both kinds of links. Use the untagged ones for credibility, and the others to stay clean.
- Stay legal: Tag sponsored content to comply with FTC rules and avoid penalties from Google or advertisers.
9. Internal Linking: Don’t Forget!
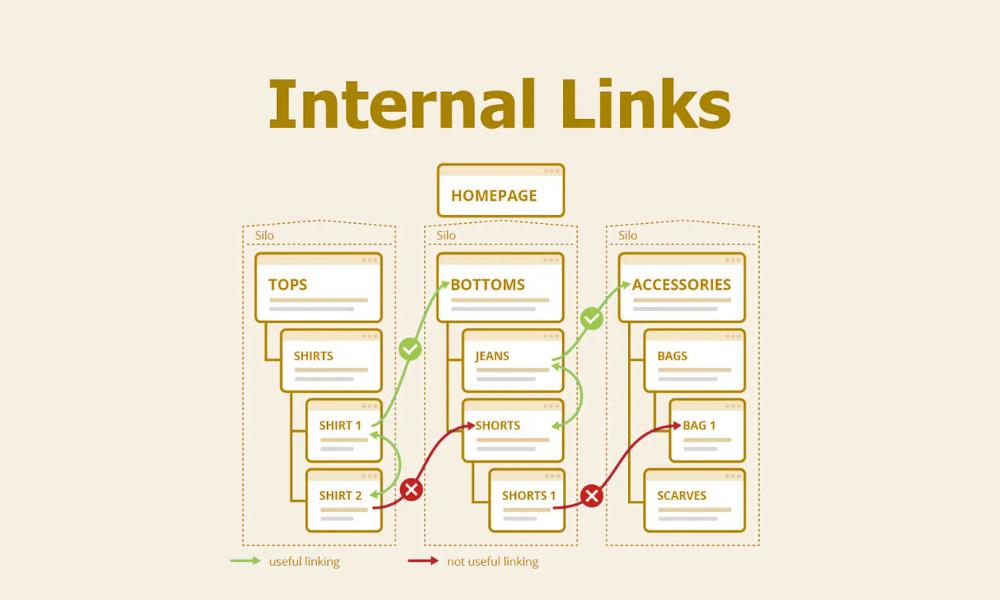
Yes, this post is about external tags—but don’t overlook internal navigation. Smart cross-linking between your own pages helps distribute authority and improve usability.
For more on optimizing site structure, take a look at my post on internal linking strategy.
10. Wrapping It Up—No Fluff
Tags are just markers. Real SEO impact comes from relevance, context, and authenticity. A few powerful references beat a flood of random citations. Focus on earning links from trusted sources, tag strategically, and let your content speak for itself.
Want a deep dive into ethical outreach or campaign measurement? Check out my guides on link‑building strategies that still work in 2025 and tracking your link efforts.